About hair loss
About hair loss
Going back as far as history will take us, baldness has been a part of getting old, which many men fear the most. Before Minoxidil (better known as Rogaine, Regaine, Avacor, Loniten or Mintop) or hair transplants, men dealt with receding hair in various ways, from magic cures to brushing their hair forward or across (the famous ‘comb-over’). Julius Caesar grew his hair long in the back and combed it to the front, as did Napoleon, George Washington wore a wig, Dwight D. Eisenhower and Sir Winston Churchill were also follically-challenged.




This truly has been an age-old problem…
Pharmaceutical companies realize that a cure for baldness means a fortune in profits for their companies and investors.
This has been enough reason for them to begin intensive research, to find that cure.
We are now much closer to understanding the mechanism of hair loss due to many new discoveries, so the hope for an early cure is certainly alive and well…
HOW DOES HAIR LOSS HAPPEN?
Hair loss problems usually develop gradually. Contrary to popular belief, baldness is not hereditary, if it was, we would be born bald. Certain tendencies and predispositions will eventually cause you to lose your hair and go bald. With the aid of modern science, Millennium Clinic can now identify what those tendencies are and compensate for them, therefore disrupting the genetic message. Our ultimate goal is to restore a normal hair growth cycle with the most up to date treatment programs and get you back to your confident self and normal life.
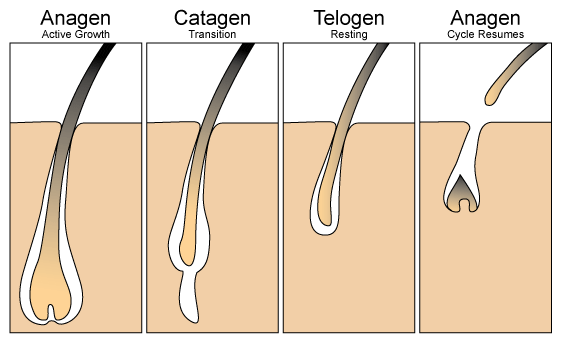
THE HAIR CYCLE:
Most men and women experience some form of hair loss/fall, thinning or baldness during their lifetime. Even during normal hair growth, there is a cycle of hair loss/fall.
A healthy follicle repeatedly goes through three phases in its life
They are: Anagen, Catagen and Telogen.
ANAGEN
In a normal scalp, about 90% of hair follicles are growing at any one time. Each follicle stays in the growing cycle for two to six years. How long an individual hair grows, depends on how long it is in the growing phase. After the growing phase, hair enters a brief transitional period.
CATAGEN
This stage begins in the 5th year. This phase typically lasts two to three weeks. Less than 1% of your hair is in this phase at any one time.
TELOGEN
The follicle then enters a resting phase. Ten percent of the hair is in a resting phase at any one time, which lasts two to three months, and at the end, the hair is shed.
When hair falls in a healthy growth cycle, a new hair from the same follicle replaces it and the anagen cycle resumes. By the 6th year, new hairs grow in a new cycle.
The number of hairs on a healthy (dark haired) scalp is approximately 100,000 to 120,000. On average, 60 to 80 hairs are lost from the scalp every day in a normal hair growth cycle.
Hair starts to recede when fewer numbers of new hairs are in the re-growth stage. As we age, the hair cycle may become disrupted and more hair is shed. In time, normal hair regrowth may stop completely and baldness will result.
In addition to the normal hair fall cycle, most men and women experience some form of hair loss or thinning hair during their life. Both men and women tend to lose hair as they age.
Some men and women start losing hair by showing thinning hair all around the scalp, while others develop a slight hair loss as a bald spot at a specific area on the head. Some individuals have complete hair loss or total baldness within a short time.
COMMON TYPES OF HAIR LOSS (ALOPECIA)
The medical term for either male or female pattern baldness is Androgenic Alopecia.
The most common cause of hair loss, over 95 % of all hair loss cases, is due to certain inherited predispositions or traits, which will eventually lead to Androgenic Alopecia. Over 66 % of all men and over 20 % of all women experience this type of hair loss during their lifetime.
Characterized by a receding hairline and/or hair loss on the top of the head, and has a gradual onset. There is a transition from large, thick, pigmented terminal hairs to thinner, shorter, indeterminate hairs and finally to short, wispy, non-pigmented vellus hairs in the involved areas
MAIN CAUSES: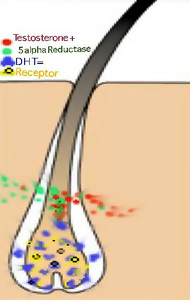
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal effect of androgen
- Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle
- Deactivation of hair matrix cells
These main causes can be broken down into 3 main factors:
- HORMONAL: Androgenic, consisting of ANDROGEN (Any of the various hormones that control the appearance and development of masculine characteristics such as testosterone).
- GENETIC: the inheritance of genes from either the mother or the father’s side of the family.
- AGE: when coupled with genetics, represents a time clock that will signal your body to produce an enzyme named 5 alpha reductase.
When the testosterone present in the follicle combines with the enzyme 5 alpha reductase, it produces Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Hair follicle receptors are sensitive to DHT and thereby start the process of male or female pattern Hair Loss.(Baldness)
- Hormone over or under activity condition such as Thyroid dysfunction may cause hair loss
- The use of steroids may add to the effects of testosterone in men’s baldness
- Medications may contribute to hair loss
- Disease may cause hair loss
- Trauma, severe physical or emotional stress, chemotherapy, surgery or anaccident can trigger Hair Loss
- Alopecia Barbae: Loss of facial hair (for a man) especially in the beard area.
- Alopecia Mucinosa: A type of alopecia which results in scaly patches.
- Anagen Effluvium: This hair loss is generally caused by chemicals such as those used to treat cancer. Initially it causes patchy hair loss, which often then leads to total hair loss. The good news is that when you stop using these chemicals the hair normally grows back (usually about 6 months later). Other drugs also can cause hair loss. Many medicines used to treat even common diseases can cause hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium: A form of hair loss where more than normal numbers of hair fall out. There is a general ‘thinning’ of the hair. Unlike some other hair and scalp conditions, it is temporary and the hair growth usually recovers.
- Scarring Alopecia: A form of alopecia, which leaves scarring on the area of hair loss.
MALE PATTERN BALDNESS
This is a receding hairline and thinning around the crown with eventual large bald area on top of the scalp.
Male pattern baldness affects many more men than women. About 25% of men begin to thin out, by the time they are 30 years old, and about two-thirds are either bald or have a balding pattern by age 60.
FEMALE-PATTERN BALDNESS
This involves a thinning throughout the scalp while the front hairline generally remains intact.
Some women also develop female pattern baldness due to genetics, age and male hormone testosterone, that tends to increase in women after menopause. The pattern is different from that of men.
Baldness was traditionally considered a masculine trait, but now, more than 30 million women in the United States alone suffer hair loss, thinning hair or baldness in some form. One in five women suffer from female hair loss. The 1999 survey by AC Nielsen, showed that hair loss now affects over 21 % of women. Despite research efforts to date, the increasing cause of hair loss in women still remains in question.
TRACTION ALOPECIA
This is a form of Alopecia, or gradual hair loss, caused primarily by pulling force being applied to the hair. This commonly results from the person frequently wearing his or her hair in a particularly tight ponytail, pigtails, braids, hair extensions etc… Traction Alopecia is a substantial risk in hair weaves, which can be worn either to conceal hair loss, or purely for cosmetic purposes.
ALOPECIA AREATA
While Alopecia Areata is baldness that typically begins with patchy hair loss on the scalp. This condition sometimes progresses to complete baldness and even loss of body hair. The hair loss tends to be rather rapid and asymmetrical and is different than male pattern baldness. Alopecia Areata affects both males and females. It tends to occur most often in children and young adults but older individuals can also be affected. The most common pattern of Alopecia Areata is one or more spots of hair loss on the scalp. There is also a form of more generalized thinning. When all of the scalp hair is lost, it is referred to as Alopecia totalis. Loss of all of the hairs on the body is called Alopecia Universalis. In this instance the bodies’ own immune system attacks the hair follicles and disrupts normal hair formation. Alopecia Areatais sometimes associated with other conditions (allergic disorders, thyroid disease, vitiligo, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis). Some cases occur within family members and indicate a genetic basis. In about half of those affected, the hair will grow within a year without any treatment. The longer the period of time of hair loss, the lower the chances the hair will grow again.
THYROID RELATED HAIR LOSS
Hormonally induced hair loss happens when an enzyme starts to convert the hormone testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. It is believed that DHT attacks the hair follicle, and shrinks it. When the follicle shrinks, it is unable to house a normal hair, the hair becomes thinner and finer, and may stop growing completely. This conversion of testosterone to DHT seems to be more pronounced in some patients with thyroid problems such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Rapid hair loss is one of the symptoms associated with thyroid problem – the thinning hair, large amounts of hair falling out in the shower or on the pillow is often accompanied by changes in the hair’s texture, making it dry and coarse.
DERMATITIS
The simple definition of Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin. Dermatitis is a very common scalp disorder that causes damaged hair. Many people think of dermatitis as having eczema but this is actually not true. Almost any rash can be thought of as a form of dermatitis, including psoriasis and skin cancer.
The scalp rash of dermatitis is itchy, red, and may or may not have distinct margins. The specific look of the rash depends on the amount of time it has been present.Acute dermatitis has blisters, sub acute dermatitis has scaling and crusting, andchronic dermatitis is a thick area of the scalp produced by excessive scratching.
Folliculitis is a bacterial infection of the hair follicles or the skin surrounding the hair. Folliculitis is probably the most common of all skin infections. Inspection usually reveals pustules on the scalp, arms and/or legs similar to those on the face of bearded men.
MEDICAL SIDE EFFECTS
Hair loss can be an unwanted side effect of many arthritis medications. Many medications for common ailments list hair loss as a common side affect. Always inquire about any and all medications being taken if you notice signs of hair loss.
See our Hair Repair and Restoration Programs
All drug free and consequently side effect free!